 Zaktualizowana została usługa dla programistów – StringEncrypt, która pozwala w prosty sposób zaszyfrować dowolne dane, generując za każdym razem unikalny algorytm szyfrowania oraz tworząca do tego automatycznie kod dekryptora w wybranym języku programowania.
Zaktualizowana została usługa dla programistów – StringEncrypt, która pozwala w prosty sposób zaszyfrować dowolne dane, generując za każdym razem unikalny algorytm szyfrowania oraz tworząca do tego automatycznie kod dekryptora w wybranym języku programowania.
Jak zwykle szyfrujemy dane?
Jeśli zależy nam na czymś co nie wymaga sporych zasobów procesora nie skorzystamy do tak trywialnego celu z szyfrowania np. AES (zapewne wymagana będzie jakaś zewnętrzna biblioteka szyfrująca lub implementacja).
W większości przypadków, każdy normalny programista napisze do tego celu własne oprogramowanie, które pobierze na wejściu ciąg niezakodowanych danych i zwróci zaszyfrowane dane. Dodatkowo zwróci je w formie pozwalającej zapisać dane w postaci kodu źródłowego języka programowania, w którym akurat tworzy oprogramowanie.
Jak szyfrować dane szybciej?
Usługa StringEncrypt pozwala:
- zaoszczędzić czas na tworzenie narzędzi programistycznych
- za każdym razem wygenerować inny algorytm szyfrujący
- wygenerowany kod nie wymaga zewnętrznych bibliotek szyfrujących
- można wybrać spośród wyjścia w C/C++, Delphi/Pascal, Java, JavaScript, Python, MASM/FASM, Haskell
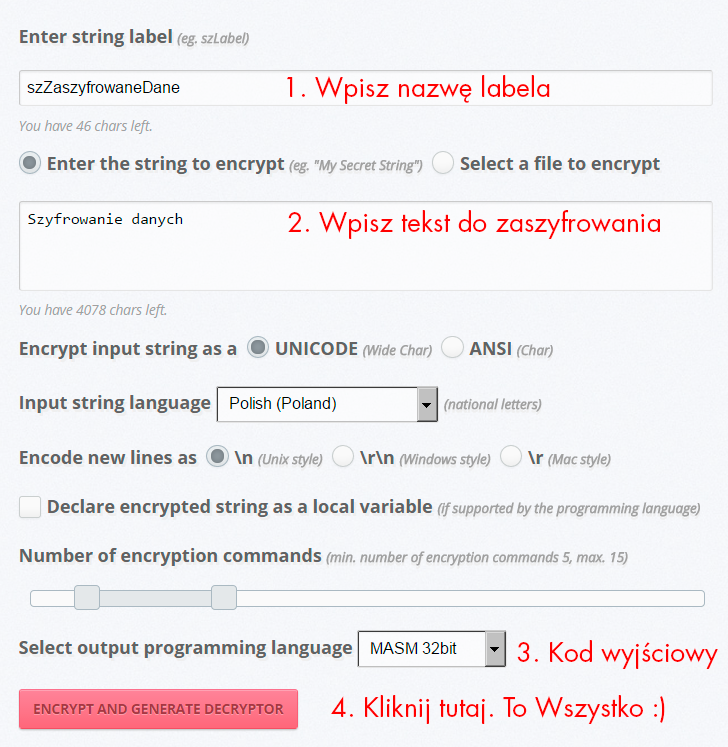
Przykład szyfrowania danych
Przykład, chcemy np. zaszyfrować string „Szyfrowanie danych”. Jak to zrobić? Na stronie głównej StringEncrypt wystarczy wpisać nazwę dla labela oraz sam tekst do zaszyfrowania i kliknąć „Encrypt and Generate Decryptor”.
Dostępnych jest kilka dodatkowych opcji jak np. wybór wyjściowego języka programowania czy sposób kodowania znaków narodowych, jeśli nasze dane takowe zawierają.
Efektem końcowym są listingi z zaszyfrowanymi danymi oraz kodem źródłowym. Przykłady tak wygenerowanych dekryptorów poniżej.
Zaszyfrowane dane oraz kod deszyfrujący w C/C++
// encrypted with www.stringencrypt.com (v1.0.0) [C/C++]
// szZaszyfrowaneDane = "Szyfrowanie danych"
wchar_t szZaszyfrowaneDane[19] = { 0xBEFE, 0xBED8, 0xBEDA, 0xBEBE, 0xBEB9, 0xBED5, 0xBEC0, 0xBEBD,
0xBEB1, 0xBECF, 0xBEBE, 0xB8FC, 0xBEC7, 0xBEB3, 0xBEB7, 0xBECD,
0xBEBE, 0xBEBA, 0xBF01 };
for (unsigned int DwvRZ = 0, sobMk = 0; DwvRZ < 19; DwvRZ++)
{
sobMk = szZaszyfrowaneDane[DwvRZ];
sobMk ^= 0xBCFB;
sobMk -= DwvRZ;
sobMk ++;
sobMk ^= 0x0CFB;
sobMk = ~sobMk;
sobMk += DwvRZ;
sobMk ^= 0x9A0E;
sobMk += 0x4ABC;
sobMk -= DwvRZ;
sobMk ^= 0xB59B;
szZaszyfrowaneDane[DwvRZ] = sobMk;
}
wprintf(szZaszyfrowaneDane);
Kod dekryptora w C# dla platformy .NET
// encrypted with www.stringencrypt.com (v1.0.0) [C#]
// szZaszyfrowaneDane = "Szyfrowanie danych"
String szZaszyfrowaneDane = "\u0236\u020F\u0210\u0227\u021D\u0222\u0226\u0224" +
"\u0239\u0220\u0224\u0279\u022B\u0220\u0231\u021C" +
"\u0226\u0201";
for (int lWdYZ = 0, AtPLU = 0; lWdYZ < 18; lWdYZ++)
{
AtPLU = szZaszyfrowaneDane[lWdYZ];
AtPLU ^= lWdYZ;
AtPLU -= 0x6403;
AtPLU ^= lWdYZ;
AtPLU ^= 0x51FE;
AtPLU += lWdYZ;
AtPLU -= 0xCF7A;
AtPLU ^= lWdYZ;
szZaszyfrowaneDane = szZaszyfrowaneDane.Substring(0, lWdYZ) + (char)(AtPLU & 0xFFFF) + szZaszyfrowaneDane.Substring(lWdYZ + 1);
}
MessageBox.Show(szZaszyfrowaneDane);
Kod dekryptujący w Delphi / Pascal
// encrypted with www.stringencrypt.com (v1.0.0) [Delphi / Pascal]
var
// szZaszyfrowaneDane = "Szyfrowanie danych"
szZaszyfrowaneDane: array[0..19] of WideChar;
VdaMu: Integer;
sveIR: Integer;
begin
szZaszyfrowaneDane[3] := WideChar($0E23); szZaszyfrowaneDane[14] := WideChar($0E36);
szZaszyfrowaneDane[6] := WideChar($0E37); szZaszyfrowaneDane[12] := WideChar($0E1E);
szZaszyfrowaneDane[8] := WideChar($0E34); szZaszyfrowaneDane[9] := WideChar($0E1E);
szZaszyfrowaneDane[11] := WideChar($0DE9); szZaszyfrowaneDane[18] := WideChar($0DD0);
szZaszyfrowaneDane[10] := WideChar($0E1D); szZaszyfrowaneDane[13] := WideChar($0E22);
szZaszyfrowaneDane[0] := WideChar($0E11); szZaszyfrowaneDane[15] := WideChar($0E2C);
szZaszyfrowaneDane[1] := WideChar($0E39); szZaszyfrowaneDane[16] := WideChar($0E31);
szZaszyfrowaneDane[17] := WideChar($0E37); szZaszyfrowaneDane[7] := WideChar($0E1C);
szZaszyfrowaneDane[5] := WideChar($0E30); szZaszyfrowaneDane[4] := WideChar($0E2C);
szZaszyfrowaneDane[2] := WideChar($0E39);
for sveIR := 0 to 19 do
begin
VdaMu := Ord(szZaszyfrowaneDane[sveIR]);
VdaMu := VdaMu - sveIR;
VdaMu := VdaMu + sveIR;
VdaMu := VdaMu - $58FA;
VdaMu := VdaMu xor sveIR;
VdaMu := VdaMu + $4B3C;
VdaMu := VdaMu + sveIR;
VdaMu := VdaMu - sveIR;
szZaszyfrowaneDane[sveIR] := WideChar(VdaMu);
end;
ShowMessage(szZaszyfrowaneDane);
Wyjściowy kod deszyfrujący w Java
// encrypted with www.stringencrypt.com (v1.0.0) [Java]
// szZaszyfrowaneDane = "Szyfrowanie danych"
String szZaszyfrowaneDane = "\uD9CD\uD9F4\uD9EF\uD9E0\uD9E4\uD9E7\uD9F1\uD9D5" +
"\uD9D8\uD9E1\uD9CB\uD986\uD9C6\uD9C9\uD9D8\uD9ED" +
"\uD9BD\uD9E2";
for (int LMSGW = 0, BZYmK = 0; LMSGW < 18; LMSGW++)
{
BZYmK = szZaszyfrowaneDane.charAt(LMSGW);
BZYmK += LMSGW;
BZYmK ^= LMSGW;
BZYmK ++;
BZYmK ^= 0xFFFF;
BZYmK -= LMSGW;
BZYmK ^= 0xFFFF;
BZYmK -= 0xD97B;
BZYmK -= LMSGW;
szZaszyfrowaneDane = szZaszyfrowaneDane.substring(0, LMSGW) + (char)(BZYmK & 0xFFFF) + szZaszyfrowaneDane.substring(LMSGW + 1);
}
System.out.println(szZaszyfrowaneDane);
Zaszyfrowane dane do wykorzystania w JavaScript (HTML)
<script type="text/javascript">
// encrypted with www.stringencrypt.com (v1.0.0) [JavaScript]
// szZaszyfrowaneDane = "Szyfrowanie danych"
var szZaszyfrowaneDane;
szZaszyfrowaneDane = String.fromCharCode(0x8C8D, 0x8C68, 0x8C6B, 0x8C84, 0x8C76, 0x8C7B, 0x8C75, 0x8C89,
0x8C82, 0x8C99, 0x8C8F, 0x8CC2, 0x8C84, 0x8C89, 0x8C9A, 0x8C91,
0x8C9D, 0x8C9A);
for (var UkhdQ = 0, LElnh = 0; UkhdQ < 18; UkhdQ++)
{
LElnh = szZaszyfrowaneDane.charCodeAt(UkhdQ);
LElnh -= UkhdQ;
LElnh -= 0xAA95;
LElnh -= UkhdQ;
LElnh += UkhdQ;
LElnh --;
LElnh ^= UkhdQ;
LElnh += 0x39C5;
LElnh -= UkhdQ;
LElnh = ~LElnh;
LElnh += 0x1C10;
LElnh ^= UkhdQ;
szZaszyfrowaneDane = szZaszyfrowaneDane.substr(0, UkhdQ) + String.fromCharCode(LElnh & 0xFFFF) + szZaszyfrowaneDane.substr(UkhdQ + 1);
}
alert(szZaszyfrowaneDane);
</script>
Szyfrowanie danych w Pythonie nie było prostsze
# encrypted with www.stringencrypt.com (v1.0.0) [Python]
# szZaszyfrowaneDane = "Szyfrowanie danych"
szZaszyfrowaneDane = [ 0x70BA, 0x70D3, 0x70D4, 0x70C7, 0x70D9, 0x70C6, 0x70DE, 0x70CC,
0x70CD, 0x70D0, 0x70C8, 0x710D, 0x70CB, 0x70C8, 0x70D5, 0x70E4,
0x70EA, 0x70E1 ]
for Zmizb in range(18):
FZBAn = szZaszyfrowaneDane[Zmizb]
FZBAn = ~FZBAn
FZBAn -= 0xF5C7
FZBAn = ~FZBAn
FZBAn -= 1
FZBAn -= Zmizb
FZBAn -= 0xF2E1
FZBAn ^= 0x73CC
FZBAn ^= Zmizb
szZaszyfrowaneDane[Zmizb] = FZBAn
szZaszyfrowaneDane = ''.join(chr(FZBAn & 0xFFFF) for FZBAn in szZaszyfrowaneDane)
del Zmizb, FZBAn
print(szZaszyfrowaneDane)
Obsługiwany jest także Haskell
-- encrypted with www.stringencrypt.com (v1.0.0) [Haskell]
module Main where
import qualified Data.Char
import qualified Data.Bits
main = do
putStrLn $ szZaszyfrowaneDane
-- szZaszyfrowaneDane = "Szyfrowanie danych"
szZaszyfrowaneDane = zipWith f [0..] [ 0x5604, 0x55DE, 0x55E0, 0x55F4, 0x55E1, 0x55E3, 0x55DA, 0x55F3,
0x55E1, 0x55E5, 0x55FC, 0x563E, 0x55FF, 0x55F9, 0x55E7, 0x55D3,
0x55E4, 0x5600 ]
where
f wvfax cxdne = let gpmae0 = cxdne
gpmae1 = gpmae0 - 1
gpmae2 = gpmae1 `Data.Bits.xor` wvfax
gpmae3 = gpmae2 - wvfax
gpmae4 = Data.Bits.complement gpmae3
gpmae5 = gpmae4 + 1
gpmae6 = gpmae5 - wvfax
gpmae7 = gpmae6 - 0xA9AA
in Data.Char.chr (gpmae7 Data.Bits..&. 0xFFFF)
Kod dekryptora w MASM
; encrypted with www.stringencrypt.com (v1.0.0) [MASM Assembler (32 bit)]
.data
; szZaszyfrowaneDane = "Szyfrowanie danych"
szZaszyfrowaneDane dw 0C08Dh, 0C078h, 0C06Bh, 0C068h, 0C0B6h, 0C061h, 0C0B9h, 0C06Bh
dw 0C05Ah, 0C067h, 0C077h, 0C042h, 0C074h, 0C077h, 0C05Eh, 0C073h
dw 0C07Dh, 0C07Ah, 0C0D0h
.code
mov edx, offset szZaszyfrowaneDane
mov eax, 19
and ecx, 0
@@:
mov bx, word ptr [edx + ecx]
sub ebx, ecx
xor ebx, 0B1C6h
not ebx
add ebx, 028B2h
not ebx
xor ebx, 0D1D9h
xor ebx, ecx
add ebx, 056FAh
not ebx
sub ebx, 0A3ADh
xor ebx, 00FA0h
add ebx, ecx
sub ebx, ecx
xor ebx, 063EBh
mov word ptr [edx + ecx], bx
inc ecx
dec eax
jne @b
push 0
push edx
push edx
push 0
call MessageBoxW
Zwróćcie uwagę, że dane zostały za każdym razem zaszyfrowane inaczej, z innym zestawem instrukcji szyfrujących, dlatego każdorazowo generowany kod jest inny.
Kod nie wymaga zewnętrznych bibliotek, bazuje na podstawowych funkcjonalnościach jakie oferują obsługiwane języki programowania.
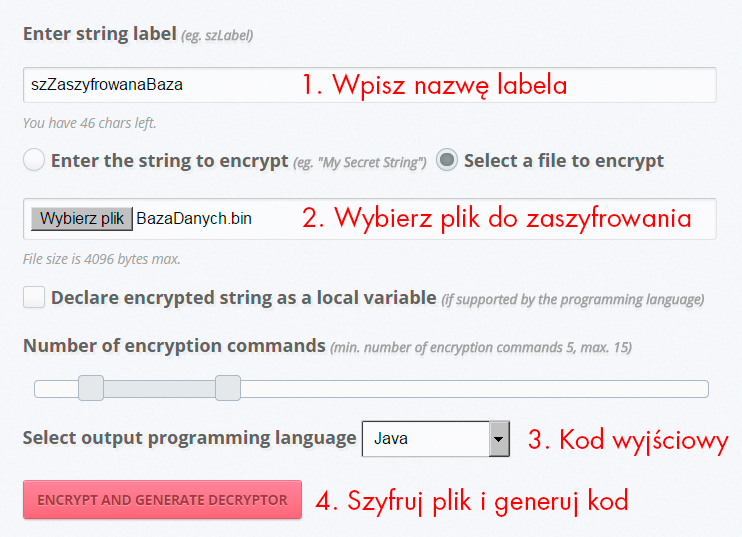
Szyfrowanie plików
StringEncrypt pozwala w równie łatwy sposób szyfrować zawartość dowolnych plików binarnych.
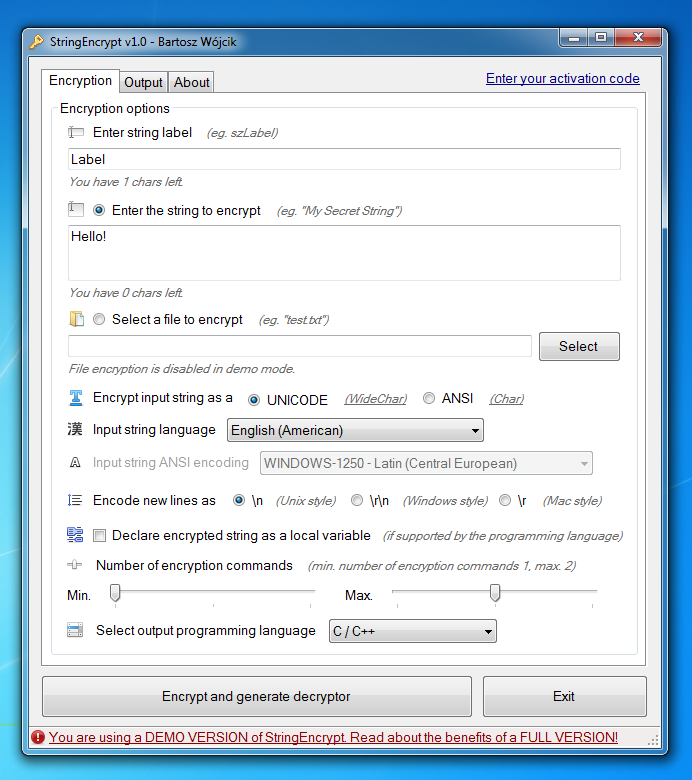
Klient końcowy dla Windows
Szyfrowanie można przeprowadzać bezpośrednio na stronie projektu, jednak istnieje również klient dla systemu Windows, oferujący tą samą funkcjonalność:
Web API
Usługa posiada również interfejs Web API bazujący na prostych zapytaniach POST, dostępne jest SDK w PHP, a jego wykorzystanie jest banalnie proste:
<?php
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// StringEncrypt.com Web API usage example
//
// Version : v1.1
// Language : PHP
// Author : Bartosz WĂłjcik
// Web page : https://www.stringencrypt.com
//
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// include main library
include ("stringencrypt.php");
//
// setup options
//
$options = array();
//
// activation code, you can leave it empty for demo version, but keep in
// mind that there are many limitations in demo version)
//
$options["code"] = "";
//
// API command to execute
//
// "encrypt" - encrypt input string or file bytes, returns array of:
//
// $result["error"] - error code
// $result["source"] - decryptor source code
// $result["expired"] - activation code expiration flag (bool)
// $result["credits_left"] - number of credits left
//
// "is_demo" - checks current activation code and returns array of:
//
// $result["demo"] - demo mode flag (bool)
// $result["label_limit"] - label limit length
// $result["string_limit"] - string/file limit lenght
// $result["credits_left"] - number of credits left
// $result["cmd_min"] - minimum number of encryption commands
// $result["cmd_max"] - maximum number of encryption commands
$options["command"] = "encrypt";
//$options["command"] = "is_demo";
//
// label name
//
// demo mode supports up to 6 chars only (64 in full version),
// if you pass more than this number, service will return
// ERROR_LENGTH_LABEL
//
$options["label"] = "Label";
//
// input string / raw bytes compression enabled, if you set it to
// true, you need to compress input string / raw bytes eg.
//
// $compressed = @base64_encode(@gzcompress($string, 9)
//
// and after encryption you need to decompress encrypted data
//
// $decompressed = @gzuncompress(@base64_decode($source));
//
$options["compression"] = false;
//$options["compression"] = true;
//
// input string in UTF-8 format
//
// demo mode supports up to 6 chars only, if you pass more
// than that, service will return ERROR_LENGTH_STRING
//
$options["string"] = "Hello!";
//$options["string"] = @base64_encode(@gzcompress("Hello!", 9));
//
// raw data bytes to encrypt (you need to specify either
// $options["string"] or this value
//
// demo mode doesn't support this parameter and the service
// will return ERROR_DEMO
//
//$options["bytes"] = file_get_contents("my_file.txt");
//$options["bytes"] = file_get_contents("http://www.example.com/my_file.txt");
//$options["bytes"] = @base64_encode(@gzcompress(file_get_contents("my_file.txt"), 9));
//
// treat input string as a UNICODE string (ANSI otherwise)
//
$options["unicode"] = true;
//
// input string default locale (only those listed below
// are supported currently)
//
$options["lang_locale"] = "en_US.utf8";
//$options["lang_locale"] = "en_GB.utf8";
//$options["lang_locale"] = "de_DE.utf8";
//$options["lang_locale"] = "es_ES.utf8";
//$options["lang_locale"] = "fr_BE.utf8";
//$options["lang_locale"] = "fr_FR.utf8";
//$options["lang_locale"] = "pl_PL.utf8";
//
// how to encode new lines, available values:
//
// "lf" - Unix style
// "crlf" - Windows style
// "cr" - Mac style
//
$options["new_lines"] = "lf";
//$options["new_lines"] = "crlf";
//$options["new_lines"] = "cr";
//
// destination ANSI string encoding (if unicode = false)
//
// only those listed below are supported
//
$options["ansi_encoding"] = "WINDOWS-1250";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "WINDOWS-1251";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "WINDOWS-1252";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "WINDOWS-1253";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "WINDOWS-1254";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "WINDOWS-1255";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "WINDOWS-1256";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "WINDOWS-1257";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "WINDOWS-1258";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "ISO-8859-1";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "ISO-8859-2";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "ISO-8859-3";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "ISO-8859-9";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "ISO-8859-10";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "ISO-8859-14";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "ISO-8859-15";
//$options["ansi_encoding"] = "ISO-8859-16";
//
// output programming language
//
// only those listed below are supported, if you pass
// other name, service will return ERROR_INVALID_LANG
//
$options["lang"] = "cpp";
//$options["lang"] = "csharp";
//$options["lang"] = "delphi";
//$options["lang"] = "java";
//$options["lang"] = "js";
//$options["lang"] = "python";
//$options["lang"] = "haskell";
//$options["lang"] = "masm";
//$options["lang"] = "fasm";
//
// minimum number of encryption commands
//
// demo mode supports only up to 3 commands (50 in full version),
// if you pass more than this number, service will return
// ERROR_CMD_MIN
//
$options["cmd_min"] = 1;
//$options["cmd_min"] = 1;
//
// maximum number of encryption commands
//
// demo mode supports only up to 3 commands (50 in full version),
// if you pass more than this number, service will return
// ERROR_CMD_MAX
//
$options["cmd_max"] = 3;
//$options["cmd_max"] = 50;
//
// store encrypted string as a local variable (if supported
// by the programming language), otherwise it's stored as
// a global variable
//
$options["local"] = false;
//$options["local"] = true;
//
// encrypt string or file contents
//
$result = stringencrypt($options);
if ($result != false)
{
if ($result["error"] == ERROR_SUCCESS)
{
// if compression was enabled, we need to
// decompress the output source code
if ($options["compression"] == true)
{
$source = @gzuncompress(@base64_decode($source));
}
else
{
$source = $result["source"];
}
// display decryptor body
echo "<pre>".$source."</pre>";
// display number of credits left
echo "<p>You have {$result['credits_left']} credits left.</p>";
// display initial number of credits
echo "<p>Initial number of credits {$result['credits_total']}.</p>";
// activation code has expired, notify user
if ($result["expired"] == true)
{
echo "<p>Your activation code has expired!</p>";
}
}
else
{
echo "An error occured (code ".$result["error"].")";
}
}
else
{
echo "Cannot connect to the API interface!";
}
?>
Strona projektu
Zachęcam do odwiedzenia strony usługi i wypróbowania https://stringencrypt.com.

Strasznie przydatny wpis dla programisty, sam z chęcią wykorzystam szyfrowanie w c++.
Zwykłych użytkowników, mogę zaprosić na swojego bloga http://www.imsafe.pl , gdzie znajduje się wpis o szyfrowaniu plików czy zdjęć gotowymi programami.